Naked Security - Computer security news, opinion, advice and research from anti-virus experts Sophos. With a Chrome Security policy you configure settings for the Sophos Chrome Security extension when it’s enrolled with Sophos Mobile.
Almost exactly a month ago, or a couple of days under an average month given that February was the short one, we warned of a zero-day bug in Google’s Chromium browser code.
Patch now, we said.
And we’re saying it again, following Google’s otherwise cheery release of version 89.0.4389.72:
The Chrome team is delighted to announce the promotion of Chrome 89 to the stable channel for Windows, Mac and Linux. This will roll out over the coming days/weeks.
We’ve never quite understood Google’s mention of rolling out updates over “days/weeks” in an update bulletin that includes 47 security fixes, of which eight have a severity level of High.
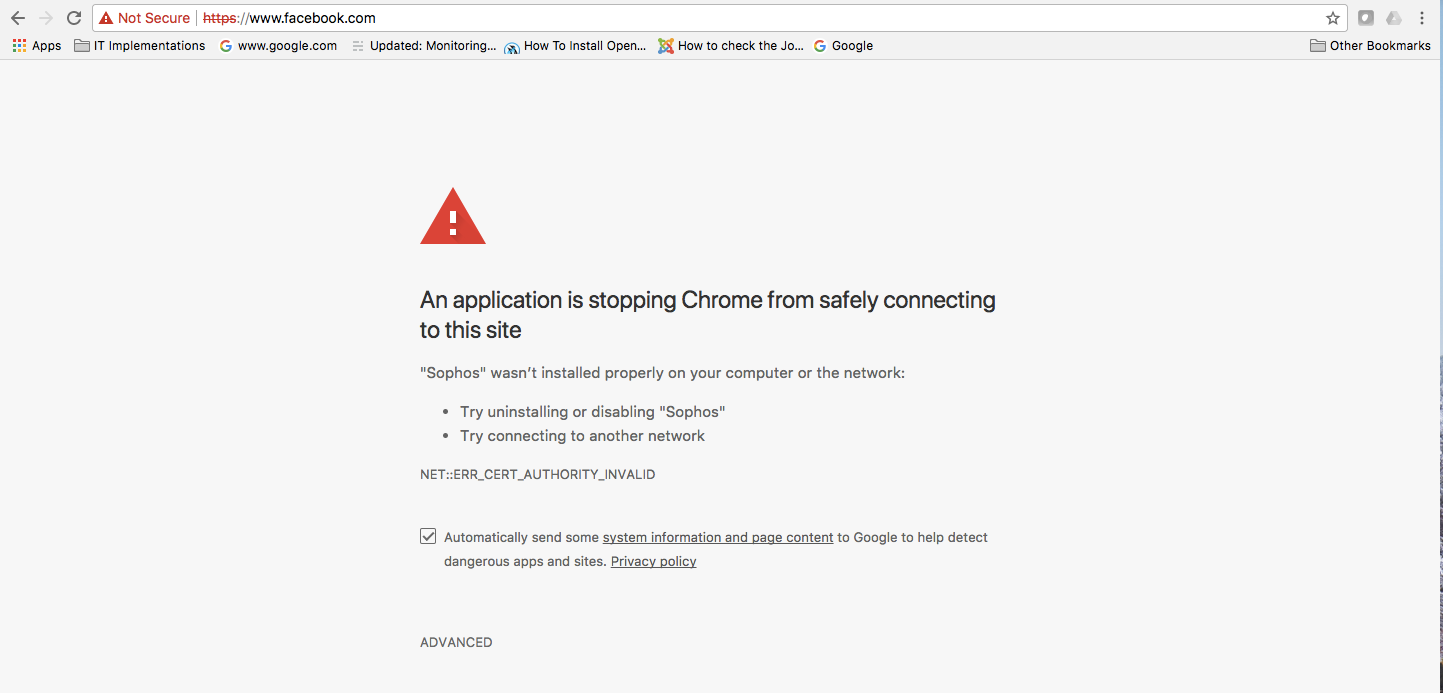
In fact, we suggest going out manually and making sure you’ve got your Chrome update already, without waiting for those day/weeks to elapse until the update finds you.
If you’re using a Chromium-based product from another browser maker, check with that vendor for information about whether their build is affected by this bug, and if so whether the patch is downloadable yet.
Object lifecycle issue in audio
Two of the eight High Severity bugs in this set of patches were apparently found in the same part of Chrome, denoted in Google’s list merely as: Object lifecycle issue in audio. Reported by Alison Huffman, Microsoft Browser Vulnerability Research.
The first bug is numbered CVE-2021-21165, reported on 2021-02-04, a month ago; the second was dubbed CVE-2021-21166, reported a week after that on 2021-02-11.
An object lifecycle issue is a jargon way of referring to what probably amounts to some kind of memory mismanagement.
The word “object” refers, very loosely, to a block of memory containing some sort of data structure, together with a list of associated programmatic functions for manipulating that data.
Managing an object’s lifecycle means, amongst other things:
- Ensuring that the memory it uses is reclaimed by the system when the object is no longer needed.
- Taking care not to reclaim and reallocate the memory while the object is still being used.
- Not doing any calculations on the object before its memory has been assigned and initialised.
- Not doing the wrong sort of calculations on the data in an object, such as trying to treat a JPEG file as a PNG, or assuming that an audio clip has 16 bits per audio sample when it only has 8 bits.
- Stopping two different parts of the program from clashing over access to the object.
Exploit in the wild
We don’t know what form these particular bugs took, given that the Chromium team’s discussion of the bugs in this release still seems to be in “keep-it-private-to-stave-off-the-crooks-a-while-longer” mode.
But we do know that at the end of this month’s bug list you will see an almost casual sentence saying that:
Google is aware of reports that an exploit for CVE-2021-21166 exists in the wild.
In vernacular language, that means “this is a zero-day bug.”
In this context, “zero-day” denotes that the crooks got there first, so that there were literally zero days on which even the fastest-patching sysadmin could have been ahead of the Bad Guys.
Who’s exploiting this bug, in which parts of the world, against whom, and with what sort of outcome, we don’t yet know.

We’re assuming that some sort of remote code execution attack (RCE) is involved, in which case this bug, when successfully triggered, could lead to crooks implanting malware on your computer without you noticing at all, let alone agreeing to download or install any files.
We’re also assuming, given that this bug apparently has something to do with audio processing, that the bug can be deliberately and remotely triggered by serving up some audio-related data via a booby-trapped web page.
What to do?
As always in a zero-day report of this sort, don’t worry too much about the exact hows and whys just yet – assume that some kind of “drive-by” RCE is possible, so that just visiting a booby-trapped site might be enough to drop malware onto your computer, and therefore patch right away.
To check what version you have, click the three-lines icon (the “hamburger menu”) in the top right corner.
Chrome Security Settings
For Chrome, go to Help > About Chrome. For Chromium simply click About Chromium.
(In either browser, you can also put the special URL chrome://settings/help into the address bar.)
The version you are looking for is 89.0.4389.72 or above.
If you aren’t up-to-date, use the Update Google Chrome option on Windows or Mac to force an update.
If you’re on Linux and your version of Chrome or Chromium is provided by your distro maker, check back with your distro for update details.
Note: If you are using Microsoft Edge, which is based on the Chromium source code but has a different version number sequence, the version to look for is 89.0.774.45 or above.
Sophos Antivirus
If you’re using Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), you can configure the Sophos Chrome Security extension to automatically enroll with Sophos Mobile when a Google Workspace user signs in to a Chrome device.
To configure Sophos Chrome Security auto-enrollment:
- On the menu sidebar, select Setup > Chrome OS setup, and then select the G Suite tab.
- Select Generate connection code.
- Configure the following settings:Option
Description Owner
Choose whether your organization owns the devices (Corporate) or the users (Personal).
Device group
The Sophos Mobile device group that you want to assign the devices to.
Chrome Security policy
Optional: A Chrome Security policy that you want to assign to the extension after the enrollment.
Only enroll on Chrome Enterprise devices
Optional: Sophos Chrome Security only auto-enrolls with Sophos Mobile on Chrome Enterprise devices.
You need to purchase the Chrome Enterprise Upgrade service from Google to enroll Chrome Enterprise devices.
For details on Chrome Enterprise, see the Google Chrome Enterprise Help.
- Click Save.
- Select Copy next to Connection code to copy the value to the clipboard.
Chrome Security Extensions

- Sign in to the Google Admin console with your Google Workspace account.
- Go to Device Management > Chrome Management > Apps & extensions.
- Optional Select an organizational unit.
Sophos Chrome Security enrolls automatically only for users in that organizational unit.
- Select the + button at the bottom right and then select Select from Chrome App Store.
- Search for Sophos Chrome Security and select Select.
- In Policy for extensions, enter the connection code from Sophos Mobile.
- In Installation policy, select one of the following:
- Force install: Install Sophos Chrome Security automatically and prevent users from removing it.
- Force install + pin: Same as Force install, and pin Sophos Chrome Security to the Chrome OS taskbar.
- Save your settings.
